The IVTD group has shown that among the commonly used human mesoderm-derived stem cell populations (isolated from distinct tissue niches), human skin-derived precursor cells (hSKPs) display the highest intrinsic cell plasticity. hSKPs exhibit properties of highly plastic neural crest (NC) stem cells. Accordingly, they are able to migrate when injected into the NC migratory stream in embryonic chicks and generate ectodermal and mesodermal progeny. This unique plasticity and NC-like characteristics imply a high potential of hSKPs for both; in vitro tissue modelling and cell therapy.
Indeed, our team has shown that upon hepatogenic in vitro differentiation, hSKPs acquire hepatic properties, yet they do not exhibit the full functionality as observed in in vivo human hepatocytes. Therefore, we are presently optimizing the differentiation methodology to boost maturation of hSKPs to fully functional hepatocyte-like cells. Nevertheless, we were able to show that hSKP-derived hepatocyte-like cells (hSKP-HPC) respond in a similar way to prototypical liver toxicants, e.g. acetaminophen (APAP) and sodium valproate (Na-VPA), as primary human hepatocytes (hHEP) in culture. Moreover, having in mind the potential clinical application of hSKPs, the efforts are also focused on the determination of the immunological profile and immunomodulating characteristics of undifferentiated and differentiated hSKP. of which no data are currently available in the open literature.
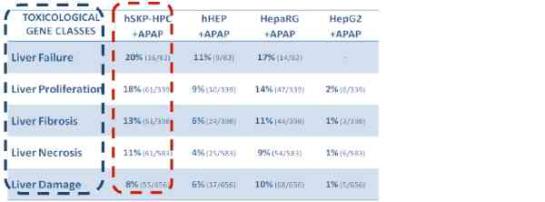
hSKP-HPC exposed to APAP identify the same toxicity gene classes as primary human hepatocytes and hepatic cell lines exposed to the same compound.
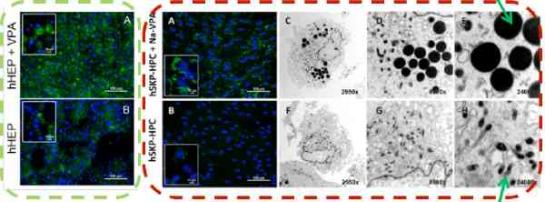
hSKP-HPC exposed to Na-VPA show accumulation of intracellular lipids. This effect is more pronounced than in hHEP exposed to the same compound.
Researchers
Prof. Joery De Kock
Dr. Robim M. Rodrigues
PhD student Alessandra Natale
Associated Projects
Relevant Publications
- De Kock J., Vanhaecke T., Biernaskie J., Rogiers V. and Snykers S. (2009) Characterization and hepatic differentiation of skin-derived precursors from adult foreskin by sequential exposure to hepatogenic cytokines and growth factors reflecting liver development. Toxicol In Vitro 23(8): 1522-1527.
- Snykers S., De Kock J., Rogiers V. and Vanhaecke T. (2009) In vitro differentiation of embryonic and adult stem cells into hepatocytes: state of the art. Stem Cells 27(3):577-605.
- De Kock J.*, Snykers S.*, Ramboer E., Demeester S., Heymans A., Branson S., Vanhaecke T. and Rogiers V. (2011) Evaluation of the multipotent character of human skin-derived precursors. Toxicol In Vitro 25(6): 1191-1202. [* equally contributing first authors]
- De Kock J., Najar M., Bolleyn J., Al Battah F., Raicevic G., Govaere O., Branson S., Jagtap S., Gaspar JA., Roskams T., Sachinidis A., Lagneaux L., Vanhaecke T. and Rogiers V. (2012) Assessment of the intrinsic pluripotency of mesoderm-derived stem cells from different niches. ALTEX 29(S1): 531-539.
- De Kock J., Najar M., Bolleyn J., Al Battah F., Rodrigues RM., Buyl K., Raicevic G., Govaere O., Branson S., Meganathan K., Gaspar JA., Roskams T., Sachinidis A., Lagneaux L., Vanhaecke T. and Rogiers V. (2012) Mesoderm-derived stem cells: the link between the transcriptome and their differentiation potential. Stem Cells Dev 21(18): 3309-3323.
- Rodrigues RM., De Kock J., Branson S., Vinken M., Meganathan K., Chaudhari U., Sachinidis A., Govaere O., Roskams T., De Boe V., Vanhaecke T. and Rogiers V. (2014) Human skin-derived stem cells as a novel cell source for in vitro hepatotoxicity screening of pharmaceuticals. Stem Cells Dev 23(1):44-55.
- De Kock J., Meuleman P., Raicevic G., Rodrigues RM., Branson S., Meganathan K., De Boe V., Sachinidis A., Leroux-Roels G., Vanhaecke T., Lagneaux L., Rogiers V.* and Najar M.* (2014) Human skin-derived precursor cells are poorly immunogenic and modulate the allogeneic immune response. Stem Cells 32(8):2215-2228. [*equally contributing last authors]
- Rodrigues RM., Sachinidis A., De Boe V., Rogiers V. Vanhaecke T.* and De Kock J.* (2014) Identification of potential biomarkers of hepatitis B-induced acute liver failure using hepatic cells derived from human skin precursors. Toxicol In Vitro 29(60):1231-1239. [*equally contributing last authors]
- Rodrigues RM. and De Kock J. (2014) Human stem cell-derived hepatocytes: breakthrough of an expedient tool for preclinical assessment of drug-induced liver injury? Archives of Toxicology 88(2):183-184.
- De Kock J., Rodrigues RM., Buyl K., Vanhaecke T. and Rogiers V. (2014) Human skin-derived precursor cells: isolation, expansion and hepatic differentiation. in Protocols in In Vitro Hepatocyte Research, Editors: Rogiers V. and Vinken M. Humana Press, Method Mol Biol, Protocols in In Vitro Hepatocyte Research, 113-122
- Rodrigues RM., Branson S., De Boe V., Sachinidis A., Rogiers V., De Kock J. and Vanhaecke T. (2015) In vitro assessment of drug-induced liver steatosis based on human dermal stem cell-derived hepatic cells. Archives of Toxicology [2015 Feb 26. Epub ahead of print]
- Rodrigues RM., Heymans A., De Boe V., Sachinidis A., Chaudhari U., Govaere O., Roskams T., Vanhaecke T., Rogiers V., De Kock J. (2016) Toxicogenomics-based prediction of acetaminophen-induced liver injury using human hepatic cell system. Toxicology letters 240 (1), 50-59
